

In a synchondrosis, the hyaline cartilage eventually converts to either bone or fibrocartilage. In a cartilaginous type of joint, there is one type of articulation that is considered immovable, the synchondrosis.Ī synchondrosis is a joint in which the articulating surfaces are close together but are bound by hyaline cartilage. An analogy to this is a wooden dowel fitting into a hole and held together by glue, with the dowel and hole representing the bony structures and the glue representing the connective tissue. Similar to the suture, the bony surfaces in the articulation are close together. The articulating edges are bound together by connective tissue. In a suture, the union of bones is bound by connective tissue.Ī gomphosis is a type of joint in which one bone fits into another bone. An analogy to this is the interlocking fashion exhibited by placing puzzle pieces together. In a fibrous joint, there are two types of articulations that are considered immovable, suture and gomphosis.Ī suture is a type of articulation in which the bones that make up the joint are close together. DescriptionĪn immovable joint can be either one of two types of joints, fibrous or cartilaginous. It is also referred to as synarthrotic (meaning immovable). The types of synovial joints are based on the shapes and can be classified in various forms: flat, spherical, ellipsoidal- and are typically consistent (embracing each other).An immovable joint is an articulation between bones in which no movement occurs. The main function of the movable joints is to allow the execution of a wide range of movements, as in the case of the knee joint or the elbow joint. They tend to be classified by the degree of their possible movement, the number of bones involved and the complexity of the joint. The main function of the joints is to allow both movement and flexibility. Externally, it is surrounded by a fibrous membrane which is capable of secreting and reabsorbing the synovial fluid (colorless, viscous substance), whose role is to fill the joints to keep them lubricated and make them move more easily. The j oint capsule is a fibrous connective tissue which ensures that the joint is secure. The joint surfaces are smooth, covered with cartilage, and gathered in a so called joint capsule. Such examples include the knee joints, elbow joints, wrist joints, shoulder joints, hip joints and ankle joints. Synovial joints, also known as movable joints, refer to the joints that are capable of moving in a variety of directions (allow mobility). Other disorders may involve cancers and birth defects (such as hip dislocation). They may caused by a fall, sudden impact or other form of trauma. Traumatic injuries are characterized by two bones separating from their meeting point. Arthritis refers to a joint condition that causes inflammation of one or more joints.
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disorder and occurs when the joints become swollen and more difficult to move.

In regards to joint disorders, the three most common types include: osteoarthritis, arthritis, and traumatic injuries. By use of scientific terminology, we speak respectively of synovial joints, synarthrosis joints and amphiarthrosis joints.
Movable joint free#
Most allow free movement, some only allow movement in certain ways and others allow no movement. Joints are classified by how much movement they allow (function) or what they are made of (structure).
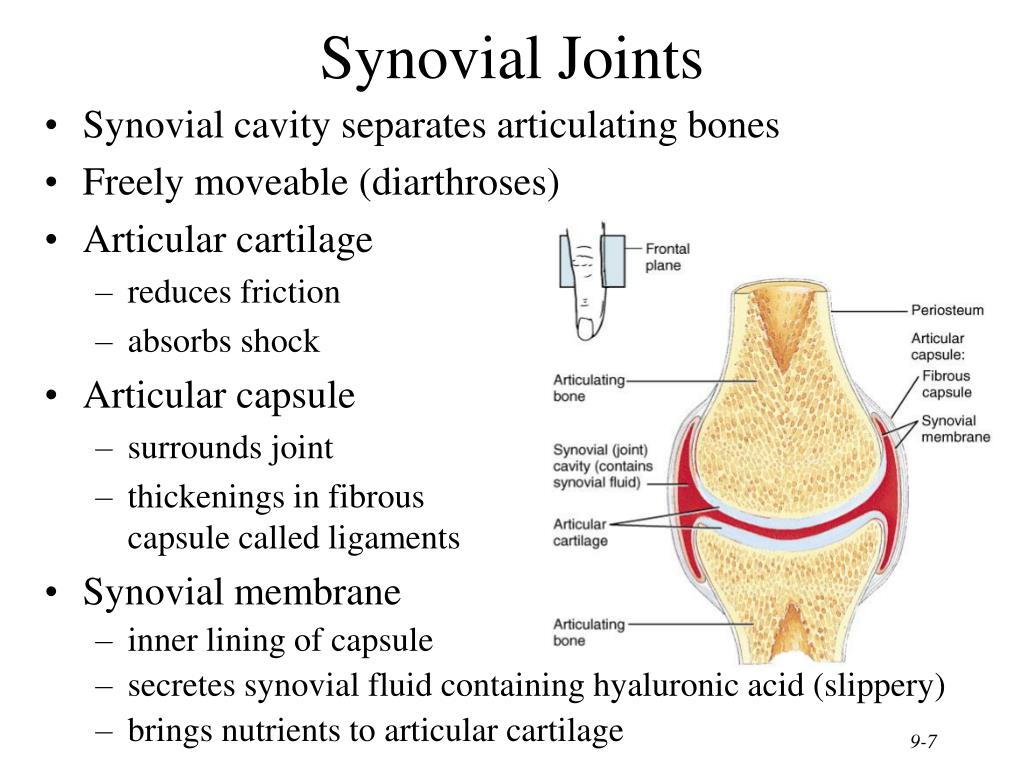
Synovial joints: knee, wrist, shoulder, elbow, ankle, and hip joints.The main bones that form the joints include the following: They make movement possible by making the skeleton flexible. Thus, articulation represents a set of elements (fibrous tissue and/or cartilage, ligaments, capsules, membranes) that regulate the connection between two skeletal segments.Ī joint is a point in the body where bones meet. In anatomy, the term " articulation" refers to an arrangement of structures that keeps two or more contiguous bony surfaces together.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
